古埃及的神祇具有不同的形态,其中就包括动物神。大型神庙的地道中存放着成百上千的动物木乃伊,尤其是象征巴斯特女神的猫、代表阿努比斯死神的狼、由王权守护者荷鲁斯幻化而成的鹰及标志托特神的朱鹮。新王国晚期以后,动物祭拜进一步风靡。这给当时的一些祭司提供了所谓的“生意”,他们饲养动物,然后把它们杀死并制作成木乃伊卖给有需求的人。......
2023-08-05
RELIGION
埃及在历史上一直是个多神论国家。沿着尼罗河从南至北分布着众多城市,它们供奉着不同的保护神:埃德富的荷鲁斯,底比斯的阿蒙,丹德拉的哈索尔,阿比多的奥西里斯,孟菲斯的卜塔等等。将不同的神祇结合在一起形成一位新的神是埃及宗教的特点之一。这些神拥有多种化身,动物即为其中一种,因此人们将动物当成神来祭拜也就不足为奇了。在古埃及的宗教信仰体系中,“国家崇拜”与“个人崇拜”共存,平行发展。对神祇的官方祭拜在神庙中举行。神庙包括公共区域和只有祭司和国王才能进入的神圣区域,一般为外墙封闭的筒式结构,由外至内,从充满自然光过渡到半明半暗的空间,最深处则陷入一片黑暗。神庙中的神祇令人难以接近,信徒们便向神的小青铜像祈祷以实现自己的愿望,这种还愿式祭拜,正是埃及人向神祇表达个人崇拜最为深切的方式。
Throughout its whole history, ancient Egypt was polytheistic.A traveller sailing along the Nile,from south to north, would encounter the numerous cities, where the local cult was devoted to different deities: Horus in Edfu, Khnum in Esna, Amun in Thebes, Hathor in Dendera, Osiris in Abydos, Ptah in Memphis, and so on.One peculiarity of Egyptian religion was that two or three names of deities could be combined to create another god or goddess.Egyptian deities could have several manifestations and many of them also had an animal form.It is no surprise then, that animals associated with specific deities were worshipped.
The official cult of the god took place in the temples, which were perfect expressions of a metaphysical vision in stone.They were divided into public and sacred areas, where only a few priests and the king could enter, and they had a peculiar telescope-like architectural structure,which gradually passed from earthly light into shadow and then darkness.The most personal and intimate type of devotion that the Egyptians could express towards the deity was the votive cult,in which objects (ex-votos) such as bronze statuettes of the deity were presented in exchange for particular favours.
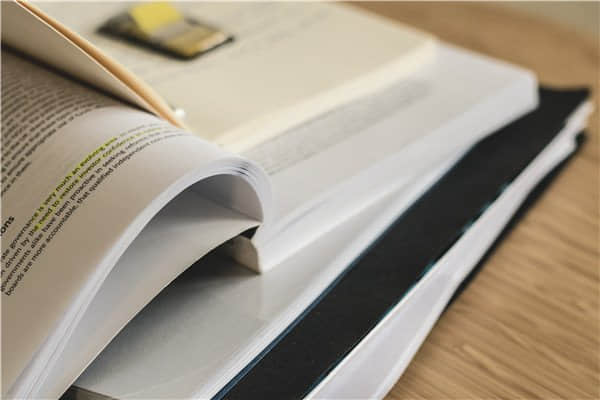
鹰神荷鲁斯神庙
有关金字塔·不朽之宫:古埃及文明的文章

古埃及的神祇具有不同的形态,其中就包括动物神。大型神庙的地道中存放着成百上千的动物木乃伊,尤其是象征巴斯特女神的猫、代表阿努比斯死神的狼、由王权守护者荷鲁斯幻化而成的鹰及标志托特神的朱鹮。新王国晚期以后,动物祭拜进一步风靡。这给当时的一些祭司提供了所谓的“生意”,他们饲养动物,然后把它们杀死并制作成木乃伊卖给有需求的人。......
2023-08-05

杭州地区与内河水文化有关的信仰有很多,多数跟依靠运河水道或海运贸易的商业有关。这其中尤以崇拜漕运神、潮神、水神、财神、仙人叔婆、路头神、龙王等信仰为盛。此外,图中冯大郎庙同样与江神祭祀有关。现如今,福建、广东和台湾地区的妈祖信仰还十分兴盛,甚至被认为是莆神。宋以来,杭州地区流行的神祇祠庙中,除前文着重提及的与运河漕运密切相关的天妃庙、金龙四大王庙、张司封庙以外,还有张王庙、五显庙、梓童庙等。......
2023-10-31

考古学家猜测,这条大鳄鱼生前可能被古埃及人当作“鳄鱼神”索贝克的化身受到崇拜,死后被制作成木乃伊,隆重下葬。对鳄鱼的崇拜,在古埃及法尤姆地区尤为突出,那里曾经沼泽丛生,鳄鱼出没。为了表达对“鳄鱼神”索贝克的崇拜,古埃及人把法尤姆的一座城市命名为鳄鱼城,并在城里修建了许多庙宇供奉索贝克。古埃及人崇拜的鳄属于鳄科,英文称crocodile,嘴唇呈V字形,闭合之时,下颚两侧的第四齿露出,紧紧与上唇贴合。......
2023-10-28

拜菩萨就得许愿,愿望实现了还得还愿——还泰山、跳猖神舞。起猖返回时,主持道士领先,五猖神与五位火把手间隔行进,五个猖神边走边挥舞钢叉,钢叉上的铜铃发出阵阵脆响,很是威风。猖神舞是旧时“还泰山”仪式中的重要内容,也是一项民间传统原始舞蹈,但该舞依附于还愿仪式,具有浓厚的迷信色彩,故已失传。......
2023-11-21
四神文化与酒泉四神造型关夫酒泉崔家南湾发现的一座魏晋墓中有非常精美的四神铺地方砖。沿对角是三条平行线把方砖分割成四个三角形的大面,四个大面依东南西北,分别是神态各异的青龙、朱雀、白虎、玄武。西汉酒泉胜迹的泉眼四壁也雕刻有四神的造型,嘉峪关也曾发现有四神的造型。再以后四神被人格化,分别给起了名字,青龙叫“孟章神君”,白虎叫“监名神君”,朱雀称“陵光神君”,玄武称“执明神君”。......
2024-10-17

埃及人喜欢在坐具、用品和神身上采用动物形象。埃及人在他们的物品或者神的身上赋予动物的相对无限能力,例如狮子、秃鹰,这些凶猛的动物能让人产生一种保护感。因此,在埃及的思想里,那些能够象征政权、财富、身份、保护神的事物被认为美的事物。象征性成为审美评判的重要因素,而动物则是象征性的重要的物质基础。然而,这种动物象征化的进程并没有延续,中间有些中断。埃及人思想里的美的观念主要由动物象征性来确定。......
2023-06-22

在唐代,观音大致定型为一手提净瓶一手持杨柳枝的女性形象,除了不同佛经有不同性别说和"现妇女身而为说法"说,中外僧人的造神活动,以及人们对妇女自然属性的认同以外,还与当时妇女地位相对崇高有关。......
2024-07-03

动物异象与中古政治——评陈怀宇《动物与中古政治宗教秩序》陈怀宇先生著《动物与中古政治宗教秩序》一书,探讨动物与中古时期政治宗教秩序的关系。但是直到目前,相对西方对于宗教与动物关系的丰富撰述,中国中古时期动物在宗教和政治中的角色和意义并未被有力阐发。然而,有关动物与中古佛教之间的相互关系的研究仍多侧重于素食和放生的主题。但是动物在中古宗教中的意义,远超于此。......
2023-11-28
相关推荐